How to override a script
By default, the standard library and package scripts are protected from changes. This is done so that there are no conflicts when new versions of the commands appear. When you modify such scripts, you must change the system name of the script and save the script under the new name.
Suppose you find a bug in the script and want to fix it. Creating a new command with a different name is not convenient, because you will have to fix all the scripts that use the original version. In this case, it is sufficient to redefine the script. To do that, you edit the original script and add the suffix .override to the system name. After that, the compiler will substitute the revised version instead of the original one. Thus, you can commit the fixed version to the repository and use it in the program without waiting for the new version to be released. If the bug is fixed during the next update, you can delete your script.
Let's consider another situation where you want to redefine a script: you want to modify the script or add some functionality. For example, there is the Write To Console command, which outputs the specified text to the console tab. Suppose you want this command to output all text to the console tab in uppercase. You can create a special command and use it, but this will not change the scripts in the standard library that use the original version. In this case, you need to override the command.
- Open the Write to Console script in the editor;
- Go to the Settings tab and add the .override suffix to the script name (write-console.override);
- Modify the script. In this case, in the Source tab you can specify
1Println( Upper(text ))
- Click the Save as button to save the modified script.
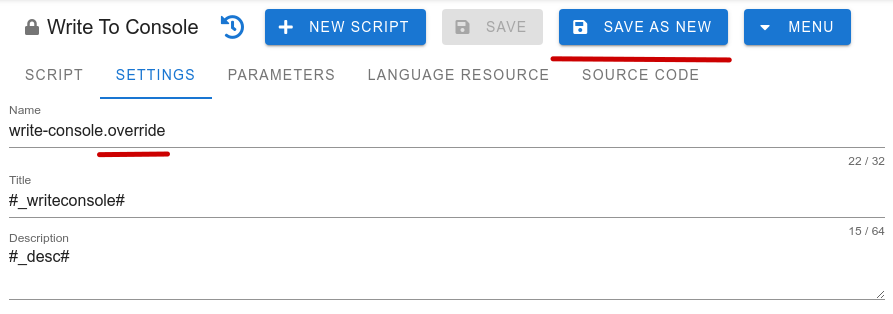
So you've redefined the command to output text to the console. Now your version will be substituted every time the original command is called and the text will be output in upper case.
If you want to disable script override, just delete the modified script or remove the .override suffix from its name.