Set Variable
The Set Variable command assigns the specified value to the variable. If the variable does not exist, it will be created. To substitute the value of a variable, use #varname#, where varname is the name of the variable.
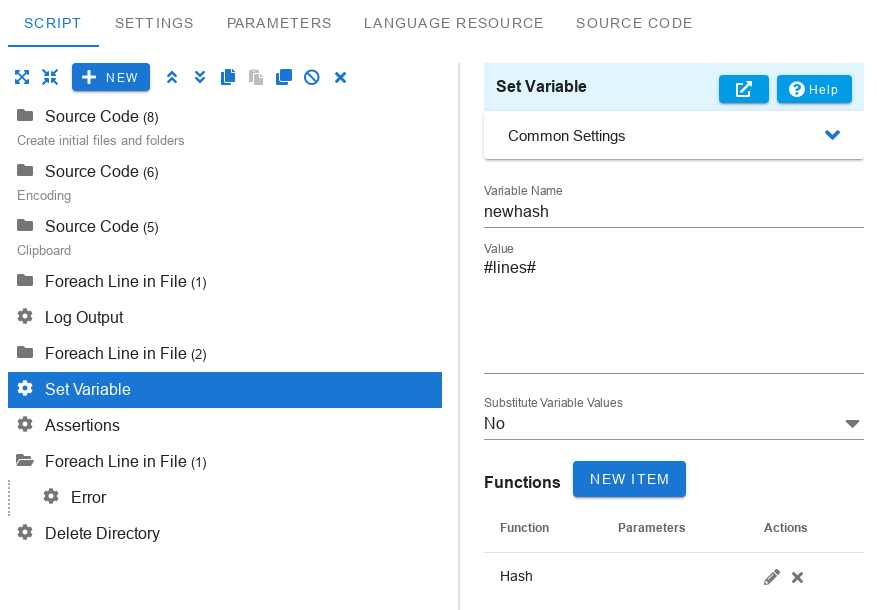
Variable name
Specify the name of the variable to which you want to assign the value.
Value
Specify the value to be assigned to the variable. It can be multi-line.
Substitute Variable Values
Whether or not to replace the values of variables when assigning.
- No - The #varname# variables will not be replaced.
- Everywhere - All #varname# variables will be replaced with their values.
- Only in the Value - Replace #varname# variables in the Value.
- Only in the Variable Name - Replace #varname# variables in the Variable Name.
By default, the variable is assigned to the specified string without substituting the variables that are included in it. For example, we assign the value #mytest# to the variable myvar. If the mytest variable changes, the next reference #myvar# will return the new value of variable mytest.
1mytest = a test 2myvar = This is #mytest#. 3#myvar# => This is a test. 4mytest = an example 5#myvar# => This is an example.
If you select Only in the Value, then the variable will be assigned a value with the replaced variables and the variable will not be changed in the future.
1mytest = a test 2myvar = This is #mytest#. 3mytest = an example 4#myvar# => This is a test.
Functions
You can specify a list of functions that will sequentially convert the current value. In this case, the Value field is the initial value. If the Value field is not specified, then the current value of the variable is taken as the initial value. You can add these functions in the order you need. The final result will be assigned to the variable.
-
Absolute Path. If the value is a relative path to a file or a directory, then it is converted into an absolute path.
-
Append. The value of the field Parameter will be appended to the current value.
-
Append Path. The path or file name in the Parameter field will be added to the current value with a / or \ separator, depending on the OS.
-
Escape Filename. Replace ':', '/', '\' with '_' as file names with such characters may be incompatible with the file system of the particular OS.
-
Filename. Get the last file or directory name from the current value.
-
Get Environment Variable. Get the value of the environment variable specified in the Parameter field. If the parameter is not specified, then the variable name is taken from the current value.
-
Hash. Calculates the hash of the current value. In the Parameter field specify the hashing method - md5 or sha256. If nothing is specified, MD5 will be used.
-
Length. The length of the current value is returned. If there is a variable with such name, the length of its value is returned. If there is an object variable, the number of elements in the array (map) or 0 is returned.
-
Lower case. Convert the current string to lower case.
-
Upper case. Convert the current line to upper case.
-
Split. Split the value into substrings formed by the separator. In the Parameter field, specify the separator string. If you want to use a space as a separator, specify #.s#. This function will assign the first substring to the current value and create an object with the same name as the variable name that will contain an array of substrings.
-
Substring. Take a substring from the current line. Specify the offset and length of the substring separated by a colon (offset:length) in the Parameter field. For example, 10:4. If you want to take a substring from a specified position to the end of the string, then specify only the offset without a colon. If the required substring is outside the string, then the substring from the specified offset to the end of the string will be returned.
-
Current Time. Get the current time in the format specified in the Parameter field. If it is not specified, the YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm:ss format will be used by default.
The result of the script